
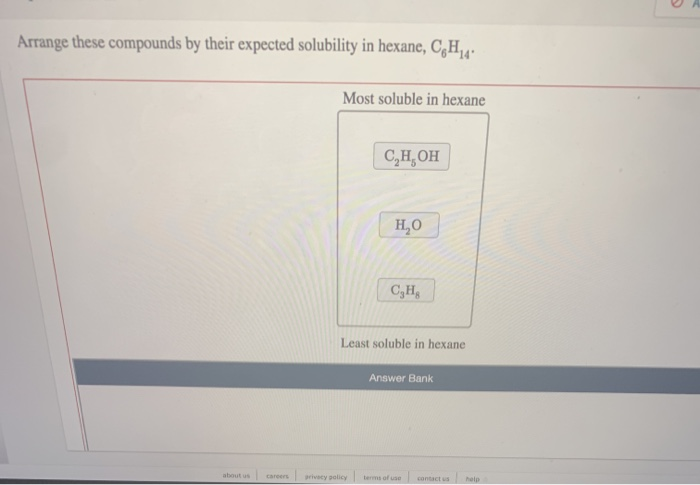
Or more of your copyrights, please notify us by providing a written notice (“Infringement Notice”) containing If you believe that content available by means of the Website (as defined in our Terms of Service) infringes one Assessment of the given interactions leads to the correct trend of increasing solubility: IV, II, I, III. III: Perchloric acid is a strong acid (stronger than nitric acid and sulfuric acid), meaning it completely dissociates in water, forming very strong ion-dipole interactions with water. II: Hydrogen bonding is present, but solubility is reduced by the presence of a multi-carbon chain, which adds significant nonpolar character to the structure. I: Hydrogen bonding dominates interaction between methanol and water (the two are miscible). In order to predict the solubilities of the given compounds, it is useful to define the primary intermolecular forces each experiences when introduced to water. Solutes that are also capable of hydrogen bonding are readily dissolved in water since they do not significantly disrupt the network of intramolecular hydrogen bonds. Water is a polar solute that forms strong hydrogen bonds (intramolecular and intermolecular), which are energetically favorable interactions. In other words, polar solvents will more easily dissolve polar solutes than nonpolar and vice versa. "Like dissolves like" is a good guiding principle to keep in mind in dealing with solubility trends. Thus, molecule IV is less volatile than molecule III, the correct answer.
As described above, attractive intermolecular interactions require more energy to overcome in order for a sample to undergo a liquid-gas phase change. Secondly, as bromine is fairly electronegative, the molecule will feature a dipole in the carbon-bromine bond, and thus a sample of IV will experience dipole-dipole attractive interactions.
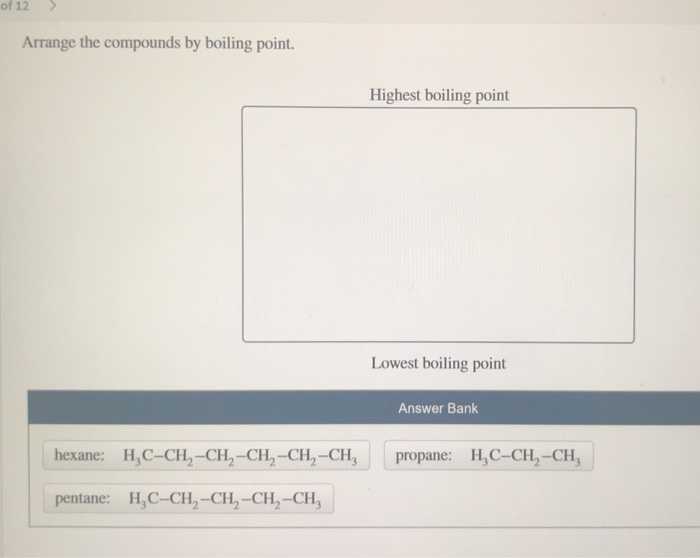
First, as bromine is much heavier than carbon, molecule IV will be much heavier than III, and will thus require much more energy to transition into the gaseous state. In other words, the hydrogen bonds will raise the boiling point and lower the volatility of these compounds.Īnswer choice IV, which features an alkyl bromide, may also be eliminated for two reasons. Hydrogen bonding is a strong attractive force, and thus more energy would have to be put into a sample to vaporize it (boil a liquid sample). These compounds have functional groups that feature polarized X-H bonds, allowing molecules in a sample of these compounds to participate in hydrogen bonding. When comparing relative volatilities of compounds, you must consider the molecular weight of a compound, as well as the intermolecular attractive forces between the identical molecules found in a sample of the compound in question.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
